As the world moves towards more sustainable building practices, the integration of fresh air systems has become increasingly important. These systems not only improve indoor air quality but also contribute to the overall sustainability of buildings. This article examines the role of fresh air systems in sustainable building design, focusing on energy efficiency, environmental impact, and occupant health.
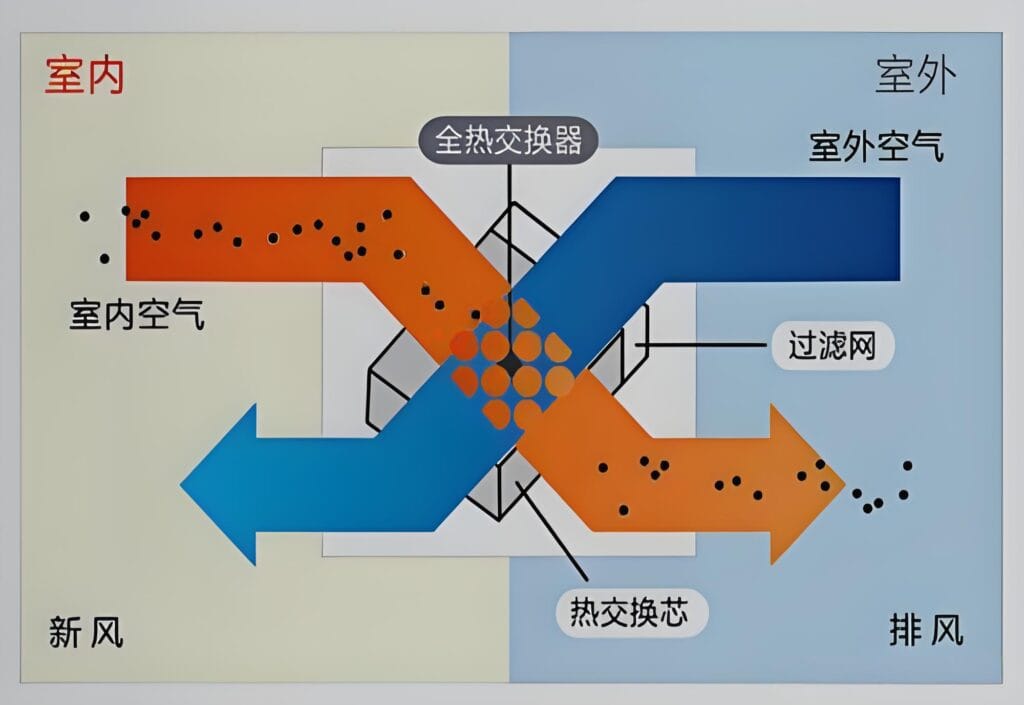
Energy Efficiency
One of the primary goals of sustainable building design is to minimize energy consumption. Fresh air systems, particularly those with heat recovery ventilation (HRV) or energy recovery ventilation (ERV) capabilities, are highly effective in achieving this goal. These systems recover heat from the outgoing stale air and transfer it to the incoming fresh air, reducing the need for additional heating or cooling.
By optimizing the ventilation process, fresh air systems help maintain a stable indoor temperature, reducing the load on HVAC systems. This not only lowers energy consumption but also extends the lifespan of HVAC equipment, resulting in long-term cost savings. Additionally, many fresh air systems are equipped with smart controls that adjust ventilation rates based on occupancy and air quality, further enhancing energy efficiency.
Environmental Impact
The environmental benefits of fresh air systems are significant. By reducing energy consumption, these systems help lower greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to the fight against climate change. Moreover, fresh air systems can be integrated with renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, to further reduce their environmental footprint.
In addition to energy savings, fresh air systems also play a role in reducing indoor air pollution. By continuously supplying fresh air and removing pollutants, these systems help create a healthier indoor environment. This, in turn, reduces the need for chemical-based air fresheners and cleaning products, which can release harmful VOCs into the air. By promoting a more natural and sustainable approach to indoor air quality, fresh air systems support broader environmental goals.
Occupant Health
The health and well-being of building occupants are central to sustainable building design. Poor indoor air quality can lead to a range of health issues, including respiratory problems, allergies, and chronic conditions. Fresh air systems address these concerns by ensuring a continuous supply of clean, fresh air.
In addition to improving physical health, fresh air systems also contribute to mental and emotional well-being. Studies have shown that improved indoor air quality can enhance cognitive function, increase productivity, and reduce stress levels. For businesses, this can translate into a healthier and more productive workforce, while for homeowners, it means a more comfortable and inviting living environment.
Conclusion
Fresh air systems are a key component of sustainable building design, offering numerous benefits in terms of energy efficiency, environmental impact, and occupant health. As the world continues to prioritize sustainability, these systems are becoming an essential feature of modern buildings. By integrating fresh air systems into building design, architects and developers can create spaces that are not only environmentally friendly but also healthy and comfortable for occupants.